Introduction
In today’s digital learning landscape, ensuring seamless content compatibility across Learning Management Systems (LMS) is crucial. SCORM-compliant courses have become the gold standard for eLearning interoperability, allowing educators, instructional designers, and businesses to create and deliver training efficiently. However, many find the process of making SCORM-compliant courses complex and intimidating.
This guide will break down how to create SCORM-compliant courses easily, making it accessible for beginners and professionals alike. Whether you’re an eLearning developer or an organization looking to standardize training, this article will provide a structured approach to creating SCORM courses without technical hassles.
What Is SCORM and Why Is It Important?
SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) is a set of technical standards for eLearning software. It ensures that digital courses function seamlessly on any SCORM-compliant LMS, enabling:
- Interoperability – Courses work across different LMS platforms.
- Reusability – Content can be repurposed without modification.
- Tracking & Reporting – Monitors learner progress and completion.
- Standardization – Ensures consistency in training delivery.
By making your courses SCORM-compliant, you future-proof your eLearning content, ensuring it remains accessible and functional across multiple platforms.
Top SCORM Versions: A Snapshot of Digital Learning
SCORM has evolved through significant versions, each enhancing the digital learning landscape.
SCORM 1.2 emerged as the first widely adopted standard, setting the foundation for tracking learner progress, scores, and session data while supporting multimedia elements like audio and video. Its straightforward nature and broad compatibility make it the most used standard today.
SCORM 2004 introduced advanced sequencing and navigation rules, enabling instructional designers to create personalized learning paths that adapt to learner performance. This version enriches data models for deeper interactions and detailed reporting.
How Does SCORM Work?
SCORM works by structuring eLearning content into standardized units that an LMS can interpret. It consists of:
- Content Packaging – SCORM courses are bundled into a ZIP file with metadata that describes the course structure.
- Run-Time Communication – When a learner launches a SCORM course, it communicates with the LMS via JavaScript APIs to track progress, quiz scores, and completion status.
- Sequencing & Navigation – SCORM allows content designers to define how learners navigate through the course.
- Reporting & Tracking – The LMS records interactions, allowing administrators to monitor user performance and engagement.
By following these principles, SCORM ensures that eLearning content is reusable, scalable, and fully trackable across different LMS platforms.
How Do You Create SCORM-Compliant Courses Easily?
1. Choose the Right eLearning Authoring Tool
A good SCORM authoring tools simplifies course creation. Here are some popular options:
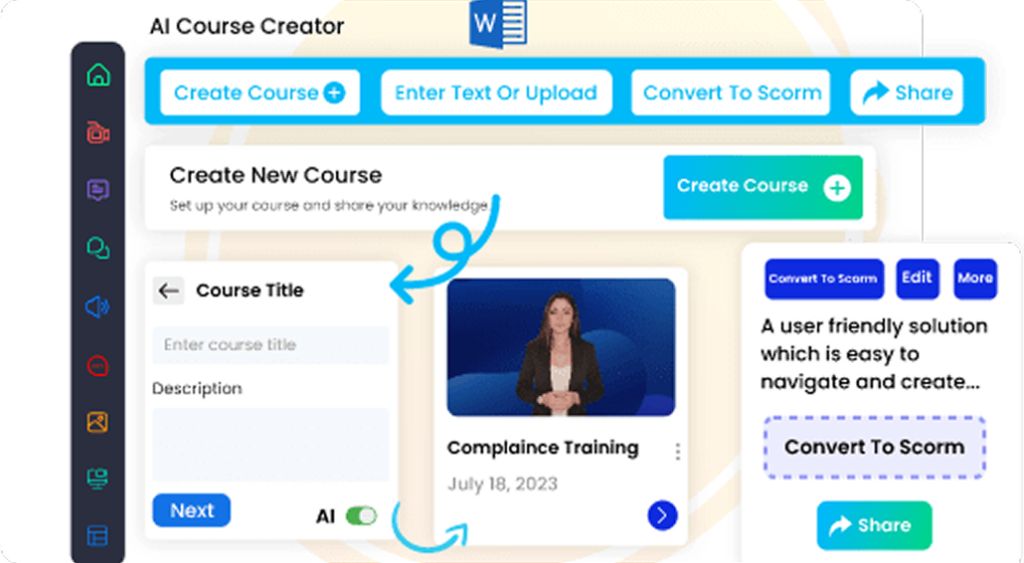
- Cognispark AI – Great for interactive and multimedia-rich courses.
- Adobe Captivate – Ideal for responsive and simulation-based training.
- iSpring Suite – Easy PowerPoint-based SCORM course creation.
- Elucidat – Cloud-based tool for team collaboration.
- Easygenerator – Beginner-friendly with simple SCORM publishing.
Tip: Select a tool that supports SCORM 1.2 or SCORM 2004 for better compatibility with LMS platforms.
2. Design Interactive and Engaging Content
Creating SCORM-compliant courses isn’t just about technical standards; engagement is key. Incorporate:
- Videos & Animations – Enhance visual appeal and retention.
- Quizzes & Assessments – Ensure knowledge checks and tracking.
- Drag-and-Drop Interactions – Improve learner participation.
- Scenario-Based Learning – Encourage real-world application.
3. Structure Your Course Properly
A well-structured course improves user experience and SCORM tracking. Follow these best practices:
- Organize Content into Modules – Use bite-sized lessons.
- Set Clear Learning Objectives – Define what learners should achieve.
- Use a Logical Navigation Flow – Keep content sequential and intuitive.
- Include Completion Criteria – Set passing scores and progress tracking.
4. Export Your Course as a SCORM Package
Once your content is ready, export it as a SCORM package using your authoring tool:
- Select SCORM Version (SCORM 1.2 or 2004).
- Define Reporting & Tracking Options (Pass/Fail, Score, Completion).
- Generate ZIP File for LMS upload.
5. Upload & Test in an LMS
To ensure your SCORM package works correctly:
- Upload the ZIP file to an LMS (Paradiso LMS, Moodle, Docebo, etc.).
- Run a Test Course to check tracking, navigation, and completion settings.
- Use SCORM Cloud (free testing tool) to validate compatibility before deploying.
Pro Tip: Always test your SCORM course in multiple LMS environments to ensure seamless functionality.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
1. Course Not Tracking Progress?
- Check LMS settings and SCORM version compatibility.
- Ensure reporting options (completion criteria) are correctly set.
2. Content Not Displaying Properly?
- Use responsive design tools for mobile-friendliness.
- Optimize media files to reduce load time.
3. SCORM Course Not Launching?
- Ensure the LMS supports SCORM 1.2 or 2004.
- Verify that the course is published correctly and compressed into a ZIP file.
Key Takeaways
- SCORM ensures eLearning content compatibility across different LMS platforms.
- Choose the right authoring tool to simplify SCORM course creation.
- Focus on engagement and interactivity to improve learning outcomes.
- Test your SCORM package before deployment to avoid technical issues.
- Use SCORM Cloud for validation before uploading to an LMS.
Conclusion & Call to Action
Creating SCORM-compliant courses doesn’t have to be complex. By leveraging the right tools and best practices, you can design engaging and trackable eLearning content with ease.
Want to streamline your SCORM course creation? Get in touch with our eLearning experts today and take your training programs to the next level!
FAQs
What is a SCORM-compliant course?
A SCORM-compliant course is eLearning content packaged to meet SCORM standards, allowing it to be consistently imported, launched, tracked, and reported across any SCORM-compliant LMS.
Which SCORM version should I choose: 1.2 or 2004?
- SCORM 1.2: Offers broad LMS compatibility and basic tracking (completion, score, session time).
- SCORM 2004: Adds advanced sequencing and navigation rules for adaptive learning paths, richer interaction data, and improved bookmarking.
Choose 1.2 for simplicity and widest support; choose 2004 if you need branching scenarios or enhanced reporting.
How do I package my course as a SCORM file?
- In your authoring tool, select “Export as SCORM.”
- Choose your SCORM version (1.2 or 2004).
- Configure reporting options (pass/fail criteria, score range).
- Generate and download the ZIP file, which will include the imsmanifest.xml manifest and all course assets.
How can I test that my SCORM package works correctly?
- SCORM Cloud: Upload your ZIP to scorm.com/cloud for free validation and detailed reporting.
- Multiple LMS Testing: Upload to at least two LMS platforms to confirm cross-platform compatibility.
- Debug Tools: Use a SCORM debugger to monitor API calls and data exchanges in real time.
Can I reuse my SCORM modules in multiple courses?
Yes. Because each Sharable Content Object (SCO) is modular and self-contained, you can import the same SCO into different course packages. This reusability saves development time and ensures consistency.