Introduction to GDPR and the Importance of Employee Training
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted by the European Union in 2018, stands as one of the most comprehensive global frameworks for data privacy and protection. Its primary goal is to empower individuals with greater control over their personal data, while imposing strict obligations on organizations that process such information. As data breaches and privacy concerns escalate worldwide, GDPR compliance has become vital for maintaining operational integrity for businesses operating within or serving customers in the EU.
The importance of GDPR for organizations cannot be overstated. It mandates rigorous data management practices and introduces hefty penalties—up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher—for non-compliance. Beyond legal repercussions, failure to adhere to GDPR can damage reputation, erode customer trust, and lead to significant financial loss.
Central to ensuring GDPR compliance is comprehensive employee training. GDPR compliance training for employees is essential, as employees are the first line of defense against data breaches, accidental disclosures, or mishandling of sensitive data. Proper training helps staff understand GDPR principles, recognize potential privacy risks, and follow best practices for data security. Additionally, well-trained employees cultivate a culture of compliance—integrating privacy-conscious behaviors into daily routines—strengthening overall data governance within the organization.
In conclusion, GDPR’s influence highlights the necessity of ongoing, targeted employee training. Equipping staff with the right knowledge and skills fosters regulatory adherence and builds trust with customers and partners in an increasingly data-driven landscape.
What is GDPR? A Brief Overview
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive law enacted by the European Union that came into effect on May 25, 2018. It represents a significant overhaul of data protection legislation worldwide, aiming to enhance individual privacy rights and create a unified legal framework for data handling across EU member states.
Built on several core principles, GDPR regulates how personal data should be processed. It covers any data relating to an identified or identifiable individual, including names, addresses, IP addresses, and online identifiers. The scope is broad: it applies to organizations within the EU and those outside that process data of EU residents or monitor behaviors within the EU.
Core Principles of GDPR
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Data must be processed legally, fairly, and openly, with individuals aware of how their data is used.
- Purpose Limitation: Data should be collected for specific, legitimate purposes and not processed in ways incompatible with those purposes.
- Data Minimization: Only necessary data should be collected and retained.
- Accuracy: Organizations must keep personal data accurate and up-to-date.
- Storage Limitation: Data should not be stored longer than necessary.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: Data must be securely processed to prevent unauthorized access or loss.
- Accountability: Data controllers are responsible for GDPR compliance and must demonstrate it.
Scope and Legal Implications
GDPR applies to data controllers and processors in the EU, organizations outside the EU serving EU residents, and entities monitoring EU behaviors. Legal obligations include appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) in certain cases, establishing processing agreements, managing consent explicitly, and notifying breaches within 72 hours. Individuals hold rights such as access, rectification, erasure, and data portability. Non-compliance can result in fines up to 4% of global turnover or €20 million, emphasizing the importance of understanding and applying GDPR principles effectively.
The Role of Employees in GDPR Compliance
Achieving GDPR compliance is a collective effort, heavily reliant on the active involvement of every employee. While organizational policies and technical measures are essential, employees serve as the frontline defenders against data breaches and non-compliance risks. Their awareness, behaviors, and adherence to procedures are crucial for safeguarding personal data and maintaining organizational trust.
Understanding Data Handling Responsibilities
Employees at all levels interact with personal data—customer information, employee records, supplier details. Each role involves understanding specific responsibilities related to data protection. For example, customer service staff must handle personal data carefully during interactions, while HR personnel must ensure confidentiality of employee information. Proper training helps staff recognize their roles in preserving data integrity, limiting access, and avoiding unauthorized disclosures.
Cultivating Data Privacy Awareness
Fostering a culture of data privacy awareness is vital. Regular training sessions and updates inform employees about GDPR principles, common threats like phishing, and best practices for security. When staff understand the importance of data protection, they are more likely to identify risks and respond appropriately, reducing accidental breaches.
Adherence to Internal Policies
Organizations should establish clear data management policies. Employees are expected to follow these—such as using strong passwords, securely disposing of sensitive documents, and promptly reporting suspicious activities. Consistent enforcement and accountability measures embed compliance into daily routines.
Impact of Employee Behavior
Employee actions directly impact GDPR compliance. Simple mistakes like sharing passwords or mishandling documents can lead to significant penalties and reputation damage. Conversely, cautious, compliant behaviors help prevent breaches and showcase organizational commitment to privacy. Data protection is a shared responsibility requiring ongoing vigilance.
Supporting Employees
Organizations should provide accessible training resources, ongoing updates, and practical guidance. Tools like simulated exercises and clear procedures bolster confidence and consistent adherence. When employees are well-informed and supported, they become proactive defenders of data privacy, strengthening the organization’s GDPR posture.
Learning Built Around Your Goals.
Discover how our courses can align with your training goals and drive real results.
Essential Components of GDPR Compliance Training
Effective GDPR training is vital for protecting data, ensuring privacy rights, and avoiding penalties. It equips employees with the knowledge and skills needed for compliance. Key components include understanding GDPR’s purpose, data subject rights, security principles, and practical handling skills.
Understanding GDPR and Its Legal Framework
Employees should grasp GDPR’s aims and scope—protecting individual privacy and establishing consistent rules. Topics include its history, objectives, legal bases for data processing, and key definitions like personal data, data controllers, and processors.
Data Subject Rights and Organizational Responsibilities
Training must cover data rights—access, rectification, erasure, portability—and organizational duties such as maintaining transparency, enabling rights requests, and preserving processing records. Employees should know how to handle data subject requests securely and efficiently.
Data Security Principles and Best Practices
Security is core to GDPR. Employees learn about confidentiality, integrity, and availability principles, measures like encryption and access controls, breach response procedures, and Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to identify and mitigate risks.
Roles of Data Controllers and Processors
Understanding organizational roles clarifies accountability. Data controllers determine processing purposes; processors act on their behalf. Both share responsibilities like cooperation, documentation, and third-party compliance.
Privacy by Design and Default
Embedding privacy into systems involves principles of proactive protection. Employees should be aware of incorporating data security from the development phase and conducting regular impact assessments.
Practical Data Handling Skills
Beyond theory, staff must develop skills such as recognizing personal data, following secure collection and storage procedures, logging activities, and appropriately responding to breaches and incidents.
Training Delivery and Continuous Education
Training must be ongoing—regular refreshers, scenario-based exercises, and assessments ensure understanding. Continuous education fosters a robust compliance mindset aligned with evolving regulations.
Looking to implement these components effectively? Browse our course catalog for customizable GDPR training programs tailored to your workforce.
Designing an Effective GDPR Training Program
A well-designed GDPR training program is crucial to establishing compliance and a privacy-conscious culture. It involves assessing organizational needs, setting clear objectives, creating engaging content, and ensuring adaptability to changes.
Understanding Organizational Needs & Setting Goals
Begin with a data audit—mapping personal data across departments—to identify risks. Define specific, measurable training objectives in line with compliance requirements, such as reducing mishandling incidents or improving data subject request responses.
Developing Relevant Content
Engage learners through real-life scenarios and role-specific modules. Focus on core GDPR topics: rights, principles, security, breach procedures. Use interactive elements like quizzes and case studies to reinforce learning.
Making Training Accessible & Adaptable
Design modular, flexible content suitable for updates. Offer multi-format delivery—videos, online courses, in-person sessions. Regular refreshers keep knowledge current and relevant.
Leveraging Technology for Delivery
Utilize Learning Management Systems (LMS), microlearning modules, and AI-powered tools to enhance engagement, track progress, and personalize learning paths. These technologies improve scalability and effectiveness across dispersed teams.
Access 100+ fully editable, SCORM-compatible courses featuring an integrated AI Tutor and an in-built authoring tool. Seamlessly compatible with any LMS, these courses are designed to elevate your training programs.
Explore Our eLearning Course Catalog
Methods and Best Practices for GDPR Training Delivery
Choosing the right delivery methods and adopting best practices enhances employee engagement and knowledge retention. Common approaches include in-person, online, and blended learning, each with specific advantages and strategies for effectiveness.
In-Person Training
Facilitated face-to-face sessions foster interaction, allow immediate clarification, and can be tailored to organizational context. Use real scenarios, group activities, and concise sessions (2–4 hours). Follow-up with refresher workshops to reinforce learning.
Online and E-Learning
Flexible and scalable, e-learning provides self-paced modules with multimedia content and assessments. Use gamification, track completion, and provide support channels to boost engagement and consistency across locations.
Blended Approach
Combining in-person and online methods offers flexibility and depth. For example, start with workshops, then assign online modules for reinforcement. Regular virtual Q&As keep engagement high.
Best Practices to Maximize Effectiveness
- Make content role-specific and relevant
- Use real-world examples
- Incorporate assessments and interactive activities
- Ensure content is clear, concise, and jargon-free
- Foster ongoing dialogue and refresher sessions
Measuring the Success of GDPR Training
Evaluating training effectiveness ensures compliance and reduces risks. Methods include assessments, feedback, and continuous improvement processes tailored to organizational needs.
Assessment Tools
- Pre- and post-training quizzes to measure knowledge gains
- Scenario-based evaluations for practical application
- Certification exams to confirm understanding
- Analytics within LMS platforms for participation and progress
Collecting Participant Feedback
Surveys, interviews, and feedback channels reveal perceptions, relevance, and clarity of material. Use this data to identify gaps and improve content.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
- Regular refresher courses and updates
- Monitor compliance incidents and audit results to assess impact
- Update training materials to reflect new regulations and feedback
- Leverage analytics to tailor interventions and target at-risk groups
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing GDPR compliance initiatives often faces obstacles such as resistance to change and complexity. Recognizing these challenges and applying strategic solutions ensures smoother adoption and sustained success.
Resistance to Change
This common challenge stems from fear, uncertainty, or perceived threats to routine workflows. Overcome this by transparent communication, involving employees early, providing adequate training, and celebrating small wins to build momentum.
Complexity of Implementation
Break down complex processes into manageable steps, use visual aids, and set clear milestones to keep efforts understandable. Regular feedback and personalized support help clarify uncertainties and sustain engagement.
Maintaining Motivation
Align training goals with organizational values, recognize efforts, foster a growth mindset, and support continuous learning. These strategies help keep staff motivated and committed over time.
The Future of GDPR Compliance and Employee Training
As data regulations evolve, organizations must anticipate and adapt to emerging trends. Automation, AI, and enhanced enforcement will shape how compliance and training are conducted, helping organizations stay proactive and resilient.
Regulatory and Technological Trends
- Stronger enforcement and international privacy law alignment
- Increased use of AI and automation for compliance monitoring
- Ongoing updates to regulations emphasizing transparency and data minimization
Impact on Employee Training
Future training will leverage adaptive platforms, microlearning, and real-time compliance monitoring tools. These technologies enable personalized, engaging, and continuous education tailored to regulatory developments.
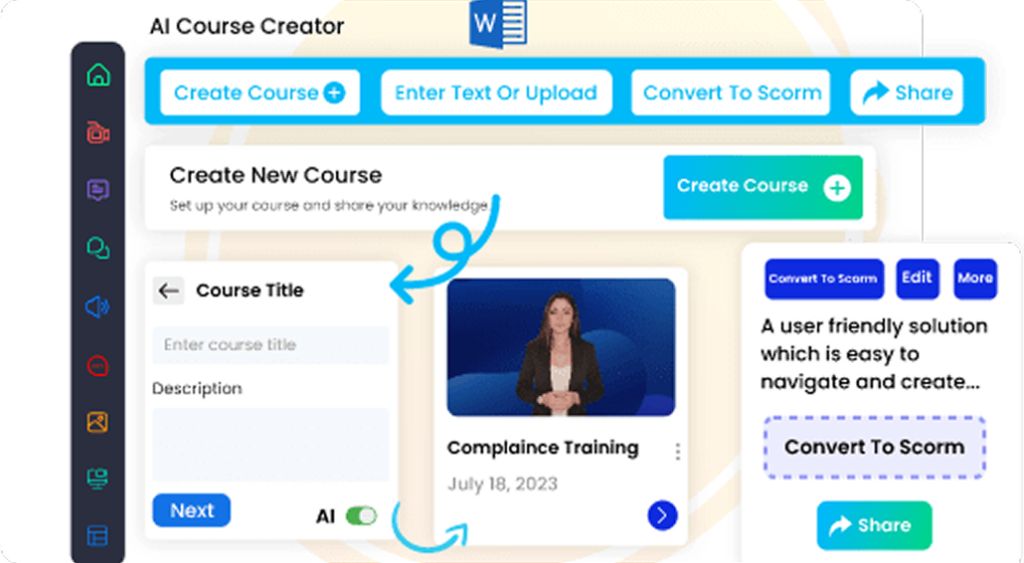
How CogniSpark AI Enhances GDPR Training & Compliance
CogniSpark AI elevates GDPR training and compliance by offering an intelligent, interactive learning environment that simplifies complex regulatory concepts. With its AI-powered tutor, learners receive real-time guidance and personalized feedback, ensuring better understanding and retention of data protection principles. The platform’s scenario-based learning immerses employees in realistic GDPR situations—like handling data breaches or managing consent—helping them apply knowledge with confidence. Organizations can also customize training content using the built-in authoring tool, aligning modules with internal policies and evolving compliance requirements. Fully compatible with any LMS, CogniSpark AI enables seamless tracking, reporting, and audit-readiness, making GDPR compliance more efficient, scalable, and employee-friendly.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Implementing effective GDPR compliance training is critical for maintaining compliance, safeguarding data, and building trust. This guide emphasized understanding core principles, role-specific responsibilities, and best practices for ongoing education. Customized, interactive, and continuous training not only reduces breach risks but also positions your organization as a responsible data steward.
Next steps include auditing current training programs, setting clear goals, and adopting scalable solutions like CogniSpark AI. Regularly updating content to reflect legislative changes and internal policies ensures your team remains compliant and prepared for future regulatory shifts.
By investing in comprehensive GDPR education and fostering a privacy-aware culture, your organization will be better equipped to navigate the evolving landscape of data protection and maintain stakeholder confidence.
Access 100+ fully editable, SCORM-compatible courses featuring an integrated AI Tutor and an in-built authoring tool. Seamlessly compatible with any LMS, these courses are designed to elevate your training programs.
Explore Our eLearning Course Catalog